
If you cannot sign in, please contact your librarian. If your institution is not listed or you cannot sign in to your institution’s website, please contact your librarian or administrator.Įnter your library card number to sign in.

Typically, access is provided across an institutional network to a range of IP addresses. If you are a member of an institution with an active account, you may be able to access content in one of the following ways: Treat the possible causes as you work through H’s and T’s.Get help with access Institutional accessĪccess to content on Oxford Academic is often provided through institutional subscriptions and purchases.

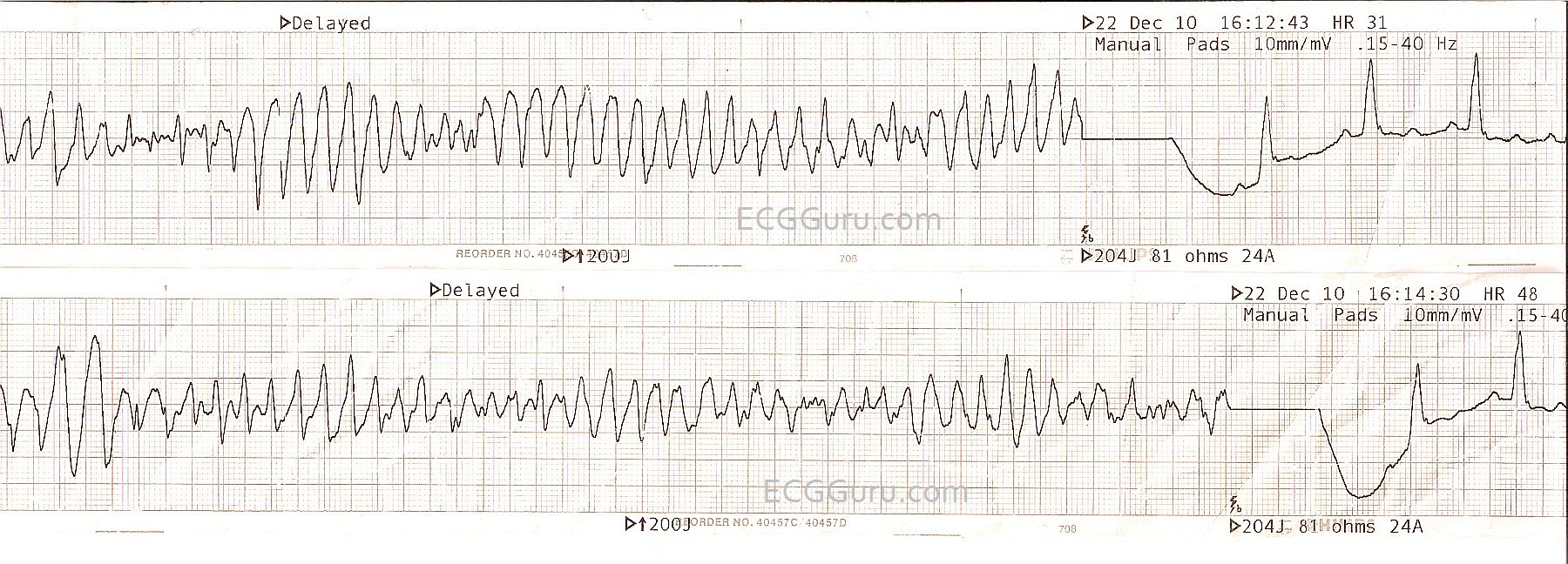
Once advanced airway is in placed, give 1 breath every 5-6 seconds (10-12 breaths/min) with continuous chest compressions. Consider securing an advanced airway, and capnography. If the rhythm becomes shockable, defibrillate. Establish an IV line and administer Epinephrine every 3-5 minutes. Monitor the ECG and check for a pulse every two minutes. Pulseless Electrical Activity (PEA) Treatment However, in PEA, there is no pulse with an orderly cardiac electrical activity similar to normal sinus, which is not a typical cardiac arrest ECG rhythm like asystole (flatline), ventricular fibrillation or ventricular tachycardia. The absence of a pulse confirms a clinical diagnosis of cardiac arrest. Therefore in PEA, it is important to treat the symptoms of the patient and not merely the rhythm displayed on the monitor. The ECG interpretation can appear the same as a normal sinus rhythm. Pulseless Electrical Activity (PEA) DiagnosisĪn electrocardiogram (ECG/EKG) device is capable of distinguishing PEA from other causes of cardiac arrest. You can also check for heart sounds by using a stethoscope for a period of no more than 10 seconds.
Make sure to check for a pulse at the carotid artery.
#VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION PULSELESS ELECTRICAL ACTIVITY ECG SKIN#
The skin may appear pallor due to no oxygen in the blood.

PEA leads to a loss of cardiac output and discontinues blood supply to the brain. Treatable Causes of Pulseless Electrical Activity (PEA)Ī patient with PEA will be unconscious with no breathing and no pulse. An ACLS practitioner should review the Hs and Ts to help identify and treat the cause of the PEA. Possible underlying causes should be identified and treated while CPR is in progress. The electrical activity is dissociated from the mechanical heart function.Ĭardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is the prime treatment for PEA. In PEA, the heart’s electrical activity is present, but the heart muscle is not responding to the electrical impulses. The electrocardiogram (ECG) interpretation displays heart rhythm activity with similarities to a normal sinus rhythm, but the patient has no palpable pulse. Pulseless electrical activity (PEA), is classified as a form of cardiac arrest.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
